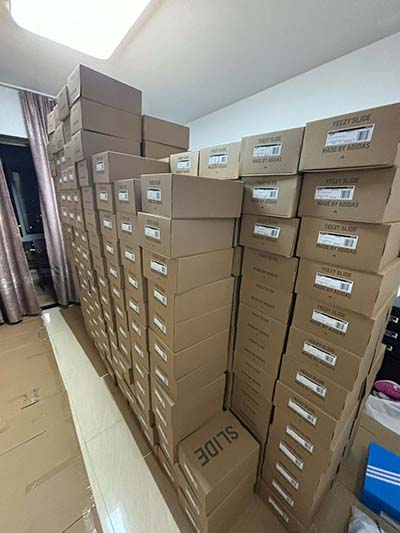
lv crypt | left ventricular myocardial mass lv crypt Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V .
Feb ruary. Mar ch. Apr il. May. Jun e. Jul y. Aug ust. Sep tember. Oct ober. Nov ember. Dec ember. Highlights. Events. Birthdays. Deaths. Weddings. Major Events. Mar 12 The Church of England ordains its first 32 female priests at the Bristol Cathedral in Bristol, England [1] Rwandan Genocide.
0 · normal Lv wall thickness
1 · myocardial wall thickness
2 · myocardial crypts
3 · left ventricular myocardial mass
4 · hypokinesis and myocardial thinning
5 · Lv perfusion is abnormal
6 · Lv end diastolic septal thickness
7 · Lv diverticulum vs aneurysm
Seamaster Professional Diver 300M Quartz (2541.80.00) Tomorrow Never Dies – 1997 Seamaster Professional Diver 300M (2531.80.00) The World Is Not Enough – 1999 Seamaster Professional Diver 300M (2531.80.00) Die Another Day – 2002 Seamaster Professional Diver 300M (2531.80.00) Casino Royale – 2006 Seamaster Professional .Inside the different cases, Omega equipped the watches with its all-new Caliber 2500. This first co-axial movement was based on the Caliber 1120 that powered the Seamaster Professional 300M that we just discussed. Omega changed the Caliber 1120 by adding the co-axial escapement and a free-sprung . See more
The first consecutive series of HCM mutation carriers systematically investigated . Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle .
normal Lv wall thickness
These “architectural abnormalities” of the left ventricle (LV) occur particularly in the .
LV outpouchings commonly include aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, and .
Left ventricular myocardial crypts were identified more commonly among . Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V . Myocardial clefts (MCs) are narrow, deep invaginations within the myocardium, . A cleft or crypt can be described as a discrete, approximately “V” shaped .
The first consecutive series of HCM mutation carriers systematically investigated by CMR 6 demonstrated an 81% prevalence of so-called crypts in the inferoseptal LV . Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, crypts have also been observed in . These “architectural abnormalities” of the left ventricle (LV) occur particularly in the septum and inferior (posterior) right ventricular (RV) insertion point and had been observed at . LV outpouchings commonly include aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, and diverticula. Myocardial clefts/crypts have uncertain clinical significance and may be in some .
Left ventricular myocardial crypts were identified more commonly among genotype-positive/phenotype-negative (G+ P−) patients with HCM (61%) compared with 261 patients .
Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V-shaped extensions of the blood pool inserting more than 50% into the compact myocardial wall . Myocardial clefts (MCs) are narrow, deep invaginations within the myocardium, localized predominantly in the basal inferior septum and left ventricular (LV) free walls . The . A cleft or crypt can be described as a discrete, approximately “V” shaped fissure extending into but confined by the myocardium, with a tendency to narrow or occlude in .
Rapid advances in cardiac computed tomography (CT) have enabled the characterization of left ventricular (LV) myocardial diseases based on LV anatomical morphology, function, density, .
Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, crypts have also been observed in seemingly healthy . The first consecutive series of HCM mutation carriers systematically investigated by CMR 6 demonstrated an 81% prevalence of so-called crypts in the inferoseptal LV . Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, crypts have also been observed in .
myocardial wall thickness
myocardial crypts
These “architectural abnormalities” of the left ventricle (LV) occur particularly in the septum and inferior (posterior) right ventricular (RV) insertion point and had been observed at .
LV outpouchings commonly include aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, and diverticula. Myocardial clefts/crypts have uncertain clinical significance and may be in some . Left ventricular myocardial crypts were identified more commonly among genotype-positive/phenotype-negative (G+ P−) patients with HCM (61%) compared with 261 patients . Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V-shaped extensions of the blood pool inserting more than 50% into the compact myocardial wall . Myocardial clefts (MCs) are narrow, deep invaginations within the myocardium, localized predominantly in the basal inferior septum and left ventricular (LV) free walls . The .
A cleft or crypt can be described as a discrete, approximately “V” shaped fissure extending into but confined by the myocardium, with a tendency to narrow or occlude in .Rapid advances in cardiac computed tomography (CT) have enabled the characterization of left ventricular (LV) myocardial diseases based on LV anatomical morphology, function, density, .
16570 EXPLORER II, Ref 16570, II 16570, 16570T, 16570-Black Movement Automatic Case material Silver, Steel Bracelet material Rubber, Satin, Snake skin, Steel Year of production 1999, 2000, 2002, 2004, 2005 Gender Men's watch/Unisex Location Germany; Italy; Japan; United Kingdom; United States of America
lv crypt|left ventricular myocardial mass